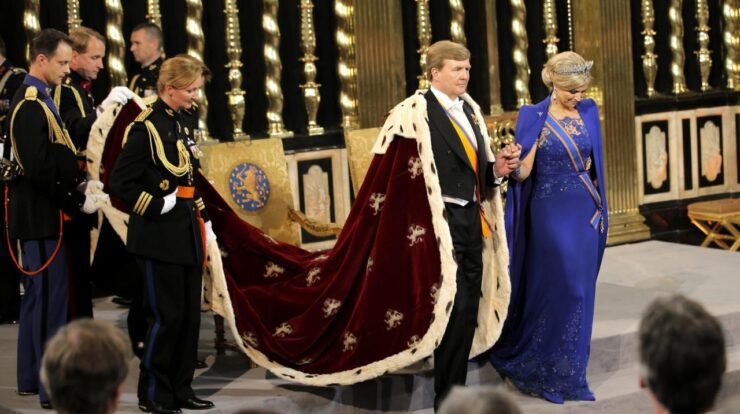
Netherlands king – The Netherlands’ monarchy stands as a testament to centuries of history, cultural heritage, and the evolution of a nation. King Willem-Alexander, the current monarch, embodies the continuity of this tradition while embracing the challenges of the 21st century.
From its origins in the Middle Ages to its present-day role, the Dutch monarchy has played a pivotal part in shaping the country’s identity and navigating its path through history.
Historical Overview: Netherlands King
The Dutch monarchy has a long and rich history, dating back to the 9th century. The first Dutch king, William I of Orange, was elected by the States General in 1581, during the Dutch Revolt against Spanish rule. The monarchy has played a central role in Dutch history ever since, providing stability and continuity during times of political and social upheaval.
Timeline of Significant Events and Monarchs, Netherlands king
- 1581:William I of Orange is elected as the first Dutch king.
- 1648:The Dutch Republic is established after the Eighty Years’ War.
- 1795:The Dutch Republic is overthrown by the French Revolutionary Army.
- 1813:The Netherlands is restored as a monarchy under William I.
- 1848:The Netherlands becomes a constitutional monarchy.
- 1948:Queen Juliana ascends to the throne.
- 1980:Queen Beatrix ascends to the throne.
- 2013:King Willem-Alexander ascends to the throne.
Current Monarchy
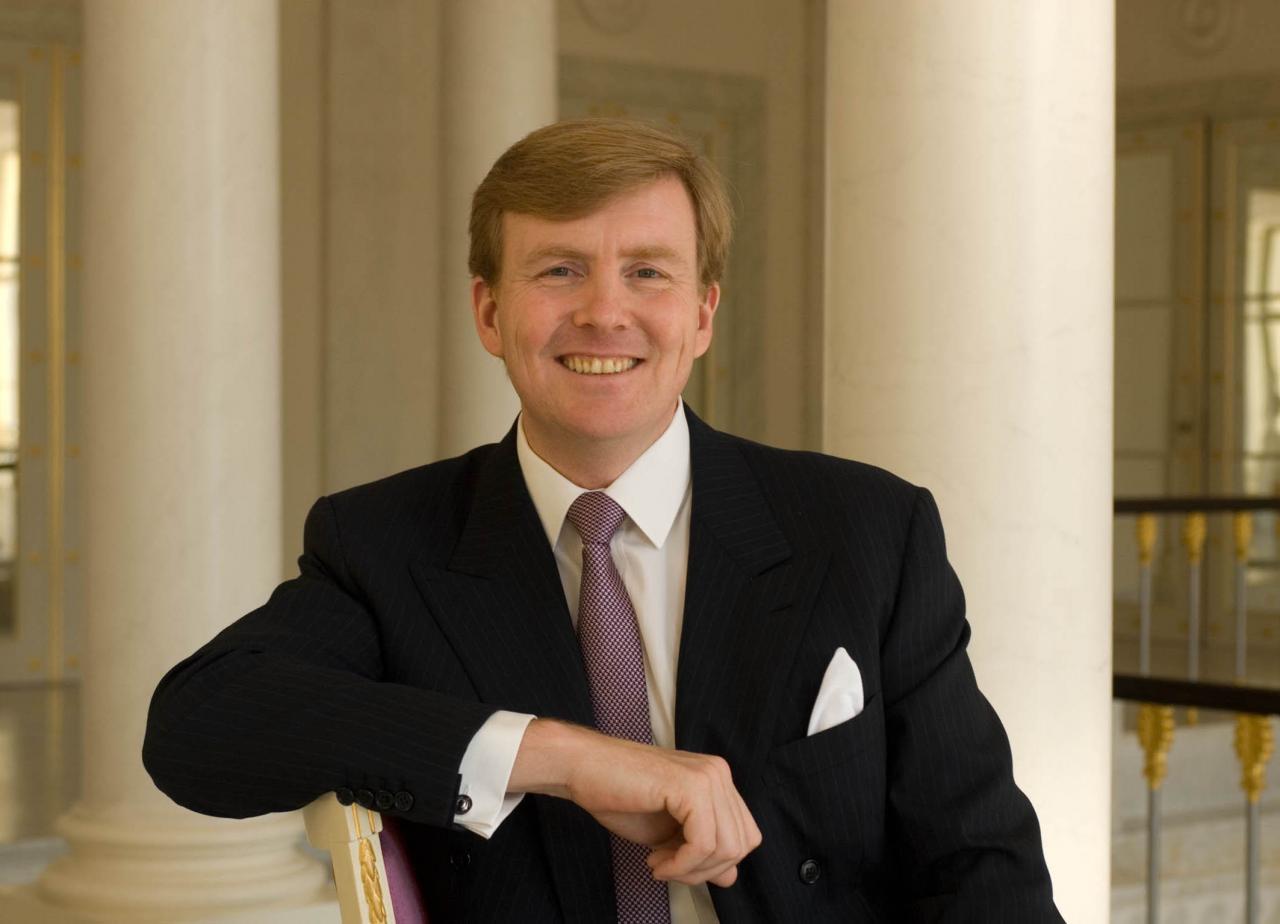

The current Dutch monarch is King Willem-Alexander. He ascended to the throne in 2013, following the abdication of his mother, Queen Beatrix. King Willem-Alexander is a constitutional monarch, which means that he reigns but does not rule. He has a number of constitutional responsibilities, including:
- Opening and closing the States General
- Signing laws into effect
- Appointing government ministers
- Receiving foreign ambassadors
The Dutch monarchy is organized into four branches:
- The Royal House:The Royal House is the core of the monarchy and consists of the King, Queen, and their immediate family.
- The Royal Court:The Royal Court is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the monarchy.
- The Council of State:The Council of State is a consultative body that advises the King on matters of state.
- The General States:The General States is the parliament of the Netherlands and is responsible for passing laws.
Royal Family and Household
The Dutch royal family is headed by King Willem-Alexander and Queen Maxima. They have three daughters: Princess Catharina-Amalia, Princess Alexia, and Princess Ariane. The royal family lives in Huis ten Bosch Palace in The Hague.
The daily life of the royal family is largely private, but they do make regular public appearances. They attend official events, visit schools and hospitals, and meet with foreign dignitaries. The royal family also plays an important role in promoting Dutch culture and traditions.
The royal household is responsible for supporting the monarchy. It consists of a number of staff members who work in a variety of roles, including:
- Private secretaries:Private secretaries assist the King and Queen with their official duties.
- Equerries:Equerries are responsible for the King’s and Queen’s transportation and security.
- Ladies-in-waiting:Ladies-in-waiting assist the Queen with her official duties.
- Household staff:Household staff are responsible for the day-to-day running of the royal household.
Royal Palaces and Estates
| Palace Name | Location | Historical Significance | Current Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huis ten Bosch Palace | The Hague | Built in the 17th century as a hunting lodge for Prince Frederick Henry | Official residence of the King and Queen |
| Noordeinde Palace | The Hague | Built in the 16th century as a royal residence | Used for official receptions and ceremonies |
| Soestdijk Palace | Soestdijk | Built in the 17th century as a summer palace for Prince William III | Former residence of Queen Juliana and Prince Bernhard |
| Het Loo Palace | Apeldoorn | Built in the 17th century as a hunting lodge for Prince William III | Now a museum |
Cultural and Social Impact
The Dutch monarchy has a significant cultural and social impact. The monarchy is a symbol of Dutch national identity and unity. The royal family is seen as a role model for the Dutch people, and they play an important role in promoting Dutch culture and traditions.
The monarchy also has a positive economic impact on the Netherlands. Royal tourism is a major industry, and the royal family helps to promote Dutch businesses and products around the world.
International Relations
The Dutch monarchy plays an important role in international relations. The King is the head of state and represents the Netherlands in diplomatic matters. He makes official visits to foreign countries and meets with foreign leaders. The King also plays a role in promoting Dutch interests abroad.
For example, in 2013, King Willem-Alexander visited China to promote Dutch businesses and to strengthen economic ties between the two countries. He also met with Chinese President Xi Jinping to discuss global issues such as climate change and nuclear proliferation.
Outcome Summary
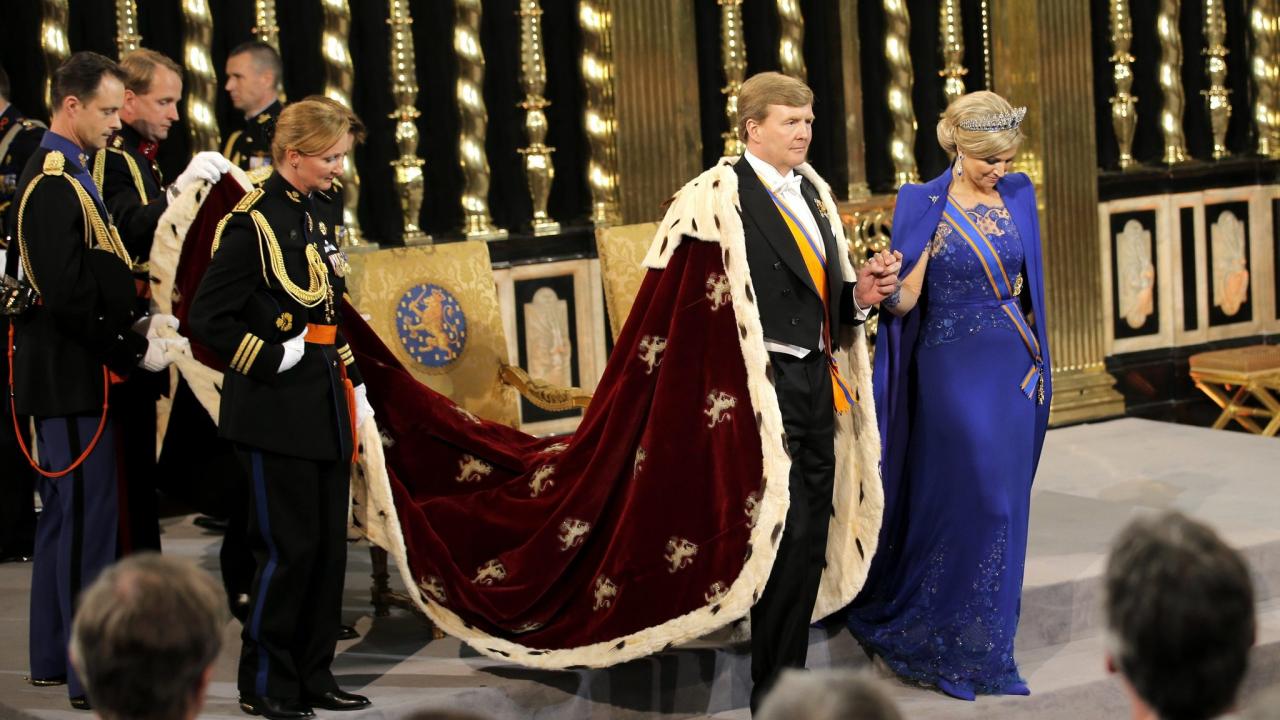

The Dutch monarchy remains a symbol of unity and tradition, while also adapting to the changing tides of society. King Willem-Alexander and the royal family continue to serve as ambassadors for the Netherlands, promoting its culture and interests on the world stage.
FAQ Summary
What is the role of the Dutch monarchy today?
The Dutch monarchy is a constitutional monarchy, with the King serving as the Head of State. While the King’s role is largely ceremonial, he plays an important role in representing the country, promoting its interests, and fostering unity.
Who are the members of the Dutch royal family?
The Dutch royal family includes King Willem-Alexander, Queen Máxima, and their three daughters: Princess Catharina-Amalia, Princess Alexia, and Princess Ariane.
What is the significance of the royal palaces and estates?
The royal palaces and estates are not only architectural marvels but also symbols of the monarchy’s history and continuity. They serve as venues for official events, state visits, and public tours, offering a glimpse into the life and legacy of the Dutch royal family.